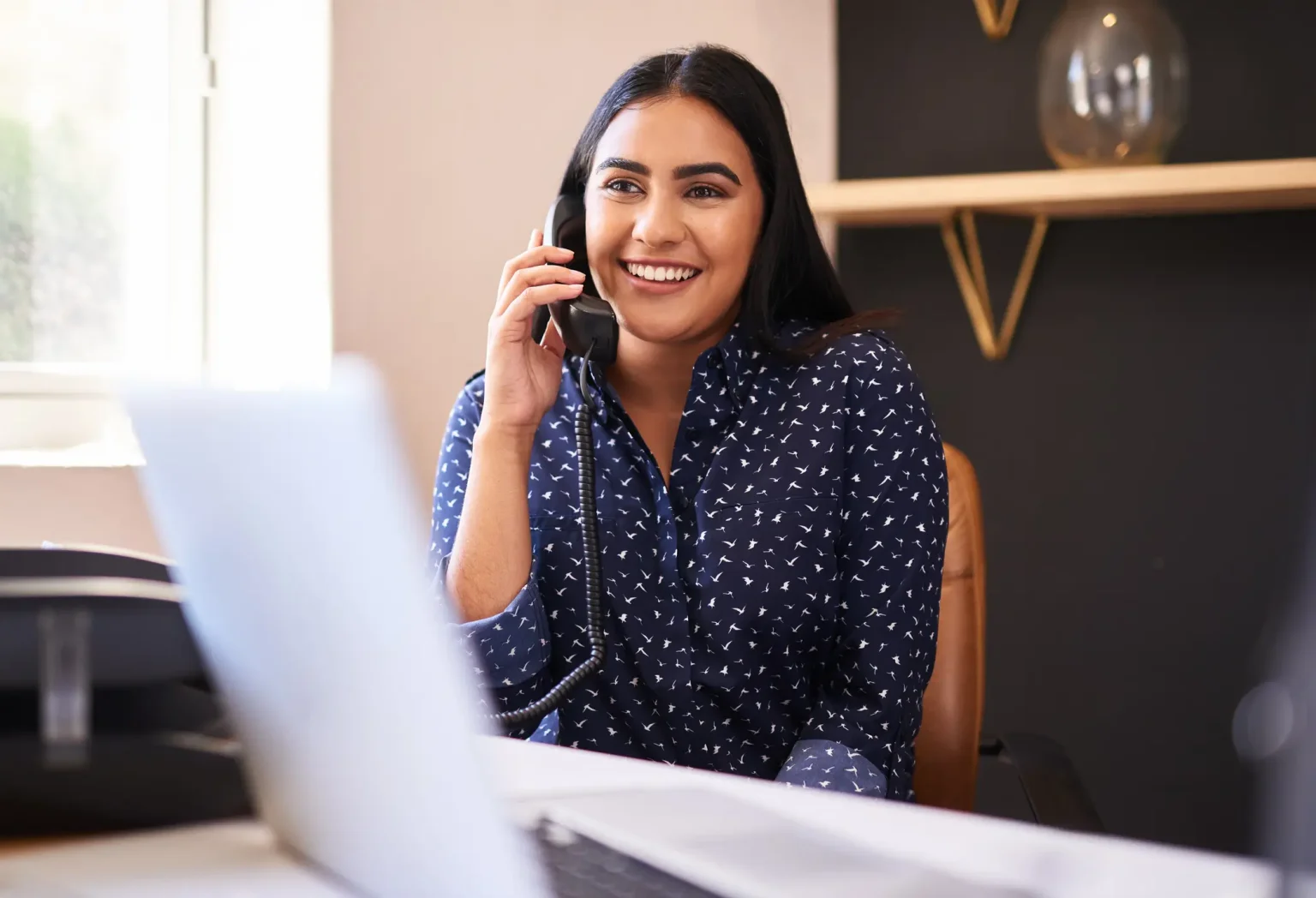

Program Path: Business
Are you looking for more than a job but a career? Getting the training you need to be an effective administrative assistant is an ideal way to start a new […]
Program Path: Health and Wellness
Are you interested in becoming a massage therapist and want to know more about massage techniques. Massage therapy is a diverse field, and there are many different massage techniques that […]
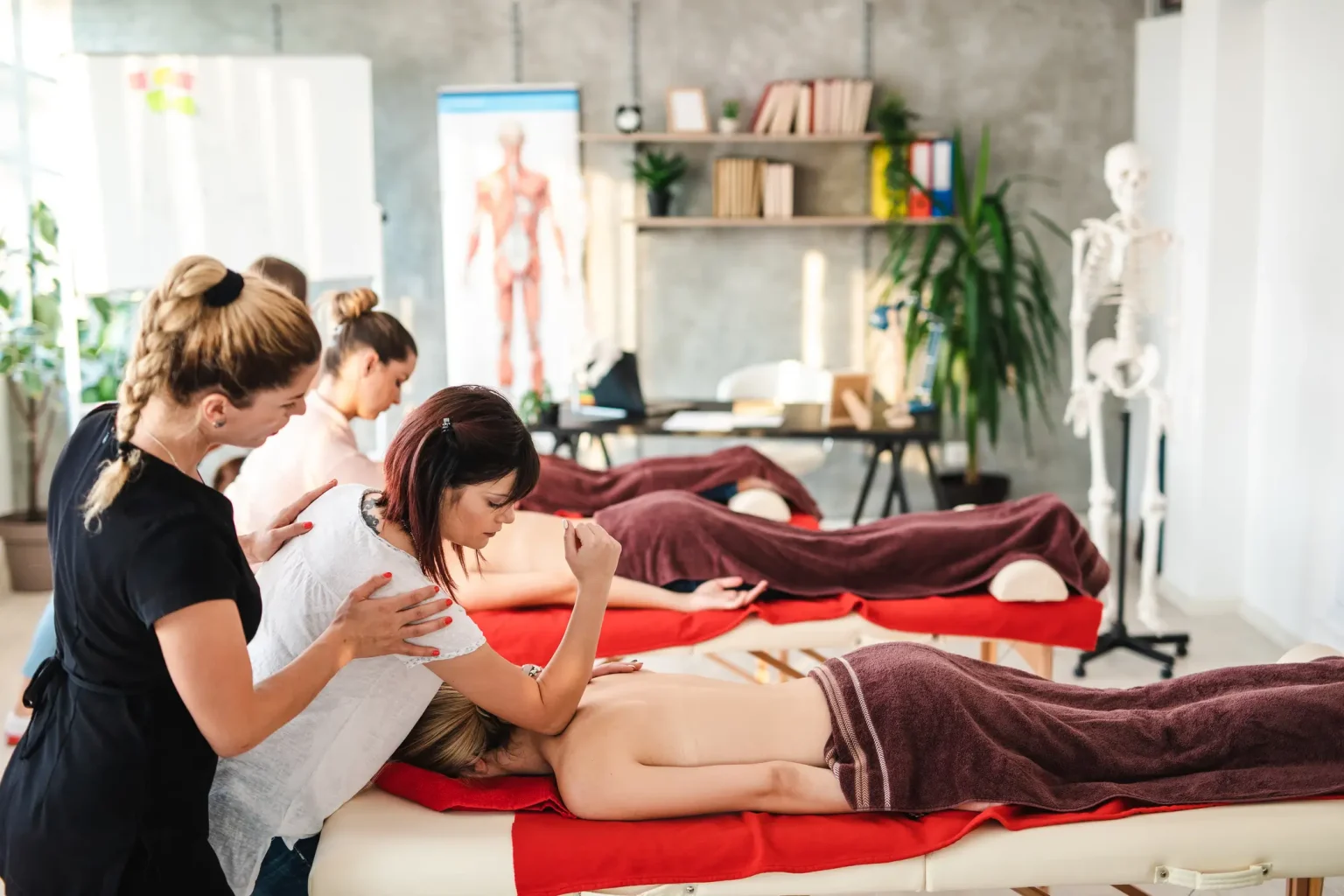
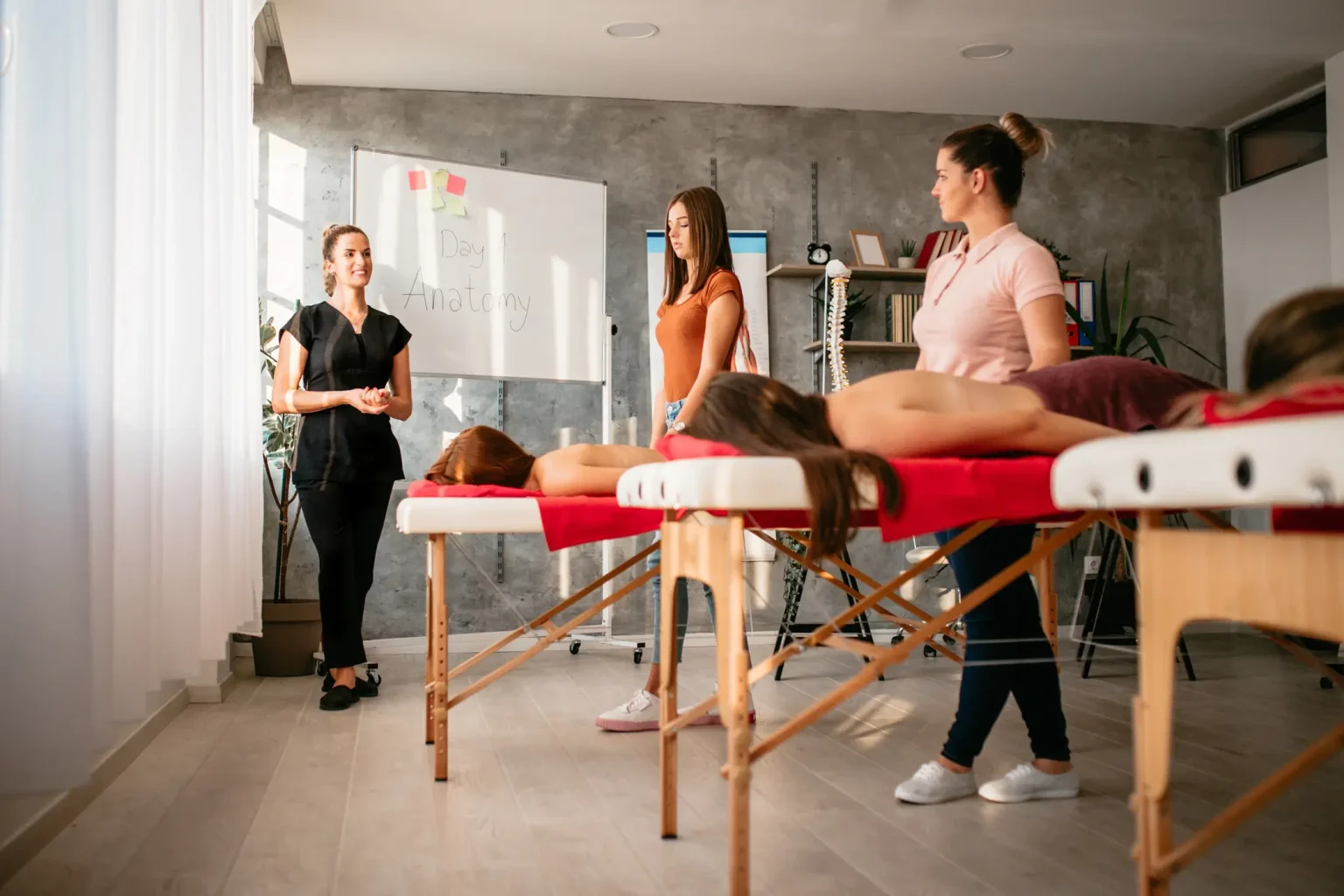


Program Path: Health and Wellness
Are you interested in becoming a massage therapist and want to know more about Swedish massage? Did you know Swedish massage forms the basis of many other types of massage, […]
Call Us Today or Complete The Form at the Top of The Page to Take the Next Step Toward Your New Career!
Gwinnett
Colleges & Institute
Gwinnett Colleges and Institute cannot guarantee employment or a minimum starting salary upon graduation; however, placement assistance is available upon successfully completing the selected program.
For state authorization and accreditation information, please refer to the location page associated with the campus you are interested in.
Disclosures and Catalogs
For Consumer Information, Disclosures, and Course Catalogs, please click the above link.
Sources and related content