
Program Path: Healthcare
Are you interested in becoming a medical assistant and wondering what an electronic health record is? What does it do and how does a medical assistant use it during their […]
Program Path: Healthcare
Medical assistants have both clerical and clinical responsibilities. Some tasks are distinctly one or the other, while others blend seamlessly together. As a medical assistant, you’ll be a jack-of-all-trades […]

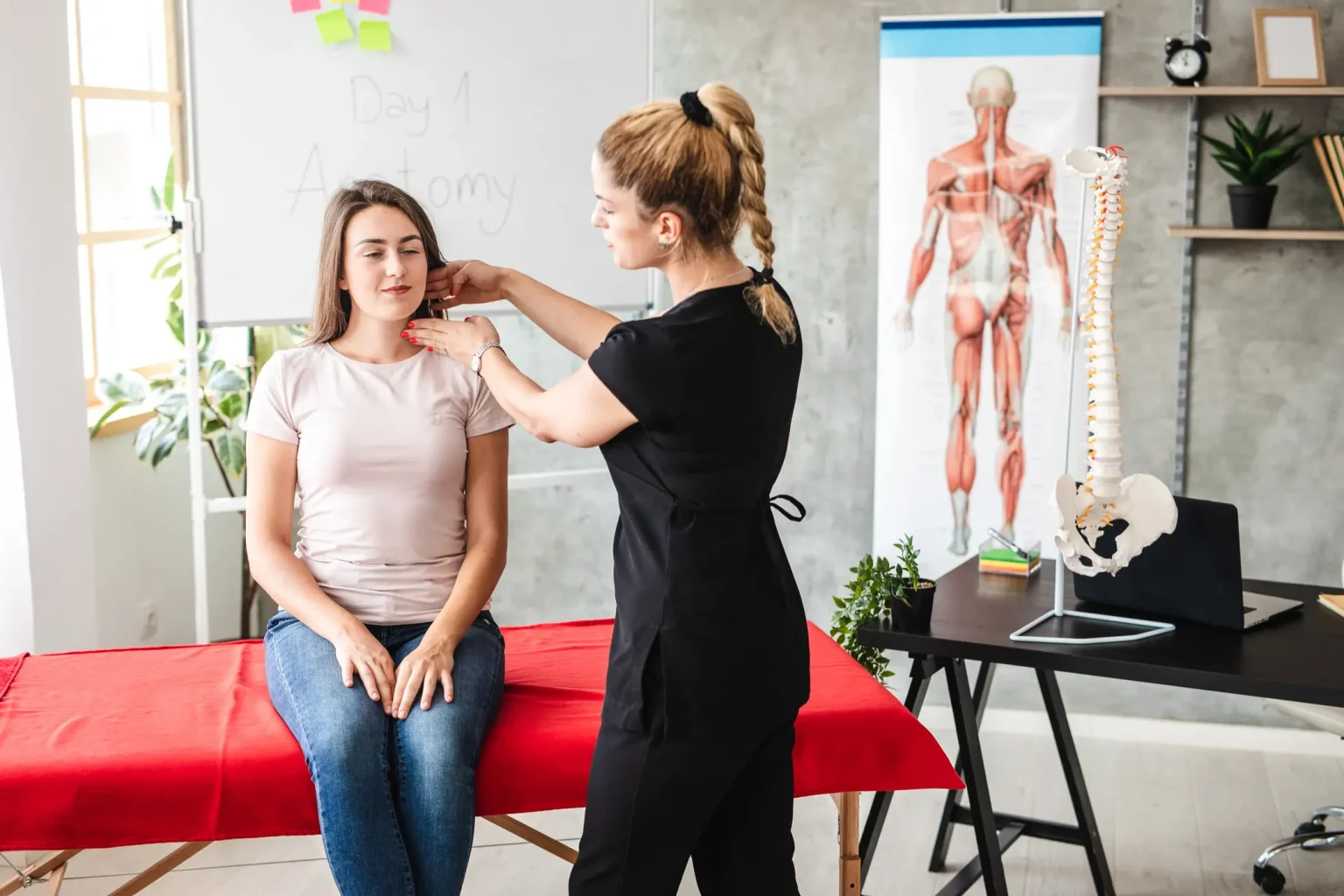
Program Path: Health and Wellness
Are you interested in becoming a massage therapist but not sure if you should go for a diploma or degree? You are not alone. Many people who are interested in […]
Call Us Today or Complete The Form at the Top of The Page to Take the Next Step Toward Your New Career!
Gwinnett
Colleges & Institute
Gwinnett Colleges and Institute cannot guarantee employment or a minimum starting salary upon graduation; however, placement assistance is available upon successfully completing the selected program.
For state authorization and accreditation information, please refer to the location page associated with the campus you are interested in.
Disclosures and Catalogs
For Consumer Information, Disclosures, and Course Catalogs, please click the above link.
Sources and related content